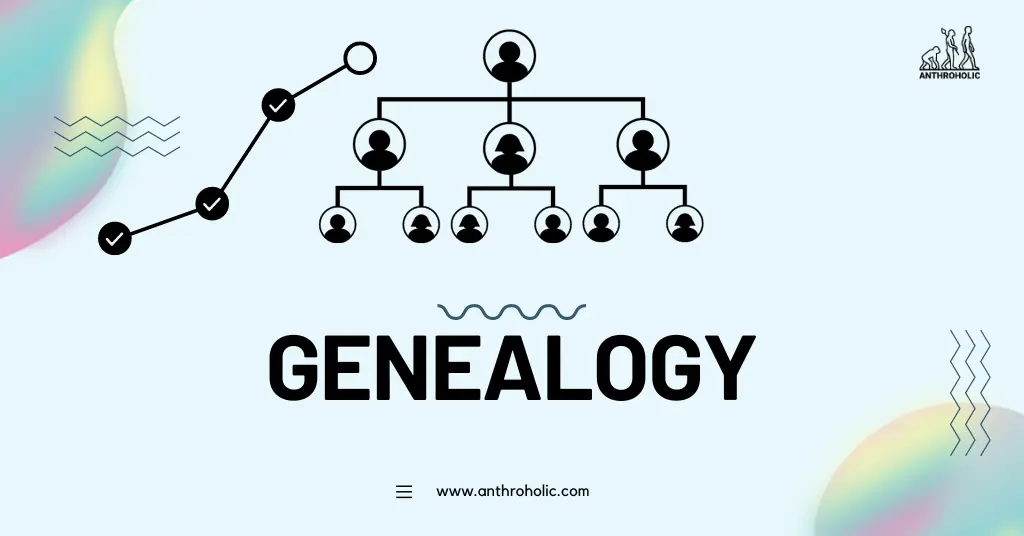
AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
G6PD
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is a genetic disorder that affects the function of red blood cells. This condition is linked to mutations on the X chromosome and is known to be the most common enzyme deficiency in humans, affecting approximately 400 million people worldwide.