AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Culture Shock
Culture shock is a common experience for people who travel or move to a new country with a different culture.
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, including human biology, culture, and society. This broad field encompasses several sub-disciplines, including cultural anthropology, linguistic anthropology, and archaeology. From exploring the diversity of human cultures to understanding the biological and evolutionary foundations of our species, anthropology provides a comprehensive understanding of what it means to be human.

Culture shock is a common experience for people who travel or move to a new country with a different culture.

A Chiefdom is a political organization in which a chief or a group of chiefs hold power over a community or tribe.

Radiocarbon dating is a method for determining the age of organic materials based on the decay of carbon-14, a radioactive isotope of carbon.

Sexual Promiscuity generally refers to engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without a committed or exclusive relationship.

Franz Boas (1858-1942) was a German-American anthropologist often called the "Father of American Anthropology."
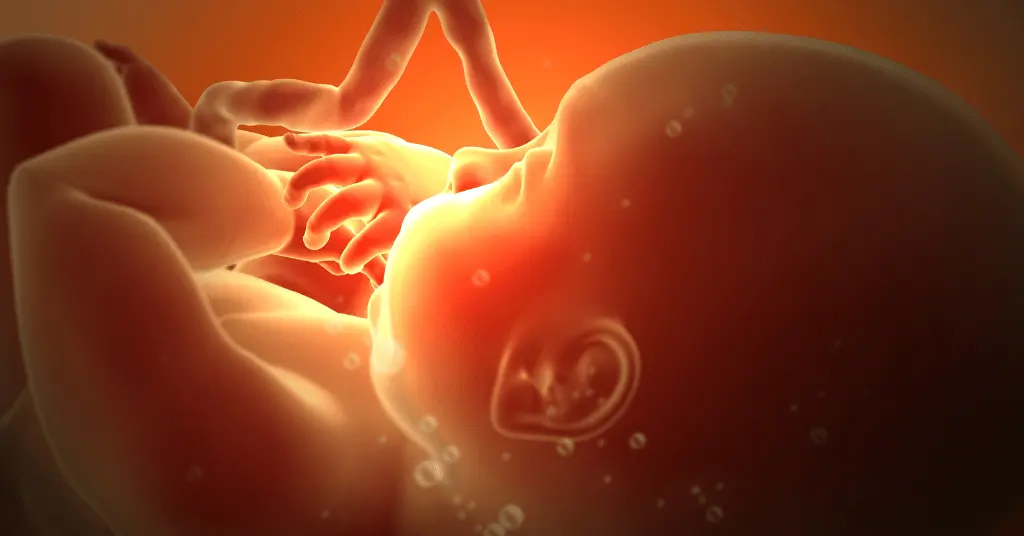
Preformationism, also known as the theory of preformation, is a biological theory that originated in the 17th century and posits that all organisms develop from preexisting miniature versions of themselves, called "homunculi."

The Theory of Recapitulation, also known as Embryological Parallelism or Biogenetic Law, is a scientific theory that proposes a parallelism between the

Anthropology and social sciences are two interconnected fields that study human behavior and society. Anthropology focuses on studying humans as a biological and cultural species

Polygamy is the marriage occurring between one person and multiple partners. While polyamory is a consistent umbrella term used for the various

Historical anthropology is a subfield of anthropology that focuses on the study of human societies and cultures over time. It examines the ways in which cultural practices, beliefs, and values have changed and evolved

Investigating the connections between people and their environments is the focus of the interdisciplinary branch of research known as environmental anthropology.

Autonomous culture, also known as self-management or self-organizing teams, refers to a work environment where employees have more control over their work and are empowered to make decisions without direct supervision.