AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
Culture and Society
Culture and Society complement one another. A shared set of beliefs, values, customs, behaviors, and artefacts that characterize a group or society is termed as culture. It encompasses linguistics, religion, cuisine, etiquettes, civility, music, and arts. Society, on the other hand, refers to a group of individuals living in a defined geographical area and sharing a culture. It is a complex system of norms, beliefs, institutions, and organizations that shape human behavior and relationships. Culture and society are interrelated and constantly shaping each other, with the former influencing the latter, and vice versa.

- Significance of studying Culture and Society
- Brief Overview
- Culture
- Society
- Connection between Culture and Society
- Social Relationships/Institutions and Cultural Practices
- Culture and Society in Cross Cultural Perspective
- History of Culture and society
- Impacts of Globalization on Culture and Society
- Conclusion
Significance of studying Culture and Society
Significance of understanding Culture and Society is crucial as it allows individuals to have a greater appreciation, respect as well as acknowledgement for the diverse ways of life that exist in the world. It aids to foster tolerance and apprehension of different cultures and ways of thinking, and can lead to improved intercultural communication and relationships.
Additionally, there are several benefits of having a comprehensive approach towards the Culture and Society of a particular group or region. For eg. :business, as it allows for more effective and culturally sensitive marketing and management strategies. It can also improve international diplomacy and aid in resolving conflicts by providing insights into the cultural and social norms that are driving the behaviour of different groups.
The impact of understanding of Culture and Society on education: it can enrich the learning episode and provide an inclusive yet broader outlook of the world. It can also be used to help address issues pertaining to society and culture, such as stereotypes, prejudice, discrimination, and inequality.
Furthermore, an understanding of Culture and Society can furnish a deeper admiration of aesthetics (the arts, including literature, music, and the visual arts) related to particular culture. It can also contribute to the multiple interpretations of historical events and political forces that have shaped the Culture and Society of the world as it is today.
Understanding Culture and Society is a crucial aspect of social and cultural anthropological development. It bridges the gaps between different groups, promotes greater adoration and respect, and contributes to a panoramic and more culturally diverse world.
Brief Overview
The anthropologists study various forms of Culture and Society, then compare them and try to arrive at commonality among them.
Culture derived from the Latin word, ‘cultura’ that means to tend, to cultivate. It is the way of life of the people. Is culture limited to human society only? The answer would be yes. Only human society has a set form of beliefs, values, customs, behaviours, and artefacts that characterise a society. Culture is a crucial component of society. Animal Society is understood without a culture factor. Yet they show some habits resembling to follow the pattern of culture.
Society is composed of individuals and groups with distinct roles, responsibilities, and habits. It is held together by shared values and norms, as well as institutions such as family, religion, and government. The culture component makes a society civilised. This is what Culture and Society is.
The equilibrium between Culture and Society is complex and dynamic. Culture informs and shapes social norms, beliefs, and institutions, while society also has a significant impact on the development and evolution of culture.
Significance of learning about Culture and Society is crucial. It helps individuals to appreciate and respect diverse perspectives, stimulate cooperative communication and relationships. However it contributes towards the betterment of a more inclusive and culturally diverse world.
Culture
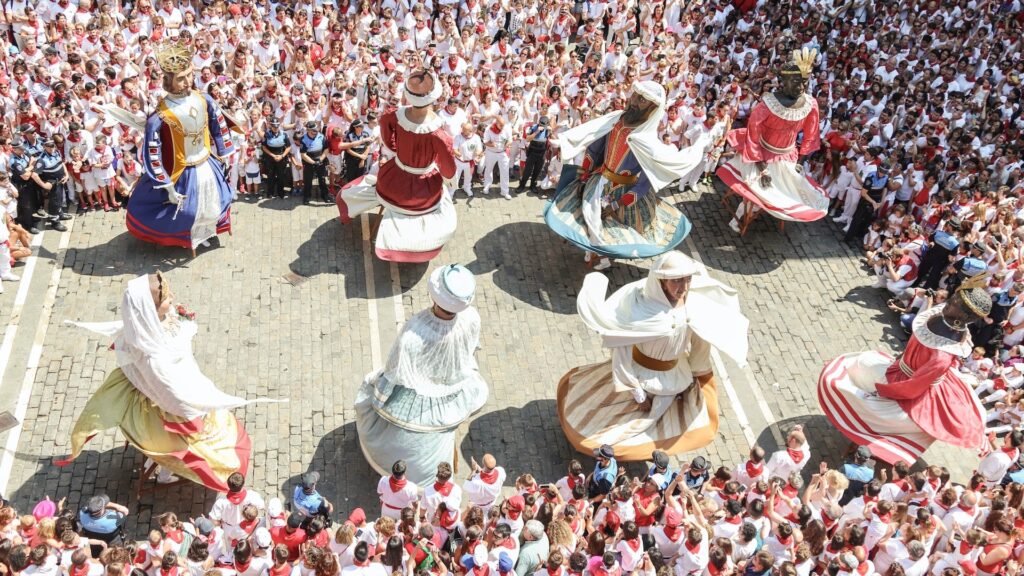

In our day to day lives, usage of the word culture is attributed to a civilized, refined behavior. However, in the terms of anthropology culture is a term referring to the behavior encompassing the personality and the way of life people in the society lead. Culture encompasses from our daily habits to our polished behavior, the way we talk, how we eat, our food, our interests, our hobbies, the dance forms, the education, customs, rituals followed, mindset of the society etc.
Culture gets cultivated and transmitted from one generation to the next, through various forms of socialization such as in a verbal form by our ancestors in the family, or through education, or media. Culture is also influenced by external factors such as globalization, migration, and coming in contact with other cultures.
Culture can be viewed as a lens through which individuals view the world and make sense of their experiences. It provides a framework for understanding and interpreting social norms, behaviors, and expectations. Culture also plays a key role in shaping an individual’s identity and shaping their beliefs and values.
Culture is not static, but is constantly changing and adapting to new circumstances with time. The dynamic nature of culture is evident in the way it influences and is influenced by other aspects of society, such as politics, economics, and the most important one nowadays technology.
Culture and Society are two fundamental sides of a coin. Both play a critical role in shaping individual as well as group identity.
Characteristics of Culture
Culture can be described as having several distinct characteristics that define its nature in shaping society. Some of the most important characteristics of culture are:
- Shared: Culture is shared by a group of individuals, such as a community, society, or nation. It is a shared system of beliefs, values, and customs that are passed down from one generation to the next, through various means.
- Learned: Culture is not something that is innate, but is learned through various forms of socialization. Society learns about it from their families, neighbors, education system etc.
- Symbolic: Culture is expressed through symbols, such as language, gestures, and artefacts, that have meaning and magnitude to members of a particular culture.
- Dynamic: Culture is constantly evolving and adapting to changing circumstances. It is shaped by historical events, technological advances, and external factors such as migration and globalization.
- Integrative: Culture provides a sense of unity and coherence for individuals, also to the crowd by integrating their beliefs, values, and behaviors.
- Diverse: Culture is diverse and varies greatly between different groups and societies. This diversity can lead to differences in beliefs, values, and ways of life, but also provides opportunities for cultural exchange and learning.
- Inclusive: Culture is inclusive, incorporating a wide range of experiences and perspectives, and providing a common bond for individuals and groups.
- Influential: Culture has a profound influence on individuals and society, shaping beliefs, values, and behaviors, and determining social norms and expectations.
Culture is a complex and multi-faceted aspect of society that is characterized by its shared, learned, symbolic, dynamic, integrative, diverse, inclusive, and influential nature.
Role of Culture in Society
The following are some of the components of culture that help define its nature and significance:
- Language: Language is the central component of Culture and Society. It is useful in communication , conveying messages, and expressing identity. It is a powerful tool for transmitting cultural knowledge, rituals and values from one generation to another.
- Religion: Culture and Religion are often used together, it can be considered as the twin of each other. Religion provides the structure for morals and values, as well as a sense of affinity and belongingness to humans for their Culture and Society . Religion can also play a role in shaping pious or social institutions, such as customs and laws.
- Customs and Traditions: Customs and traditions are a crucial part of Culture and Society, providing a sense of continuity and stability over time. They include practices such as holidays, rituals, and social patronage, and can vary greatly between different cultures.
- Art and Literature: Culture is expressed through the arts, including music, dance, theatre, and literature. These forms of expression provide a means of capturing and conveying cultural awareness and values, as well as providing a source of entertainment and recreation. It also provides recognition.
- Material Culture: Material culture refers to the physical objects and artefacts that are created and used by members of a culture, such as tools, clothing, and housing. Material culture reflects the beliefs, and practices of a culture, and provides a glimpse into its history and its further development.
- Knowledge and Education: Culture is also shaped by knowledge and education, which provide individuals with a basis for understanding their world and shaping their beliefs and values. Education can take many forms, including formal schooling, apprenticeships, and self-study.
- Economic Systems: Economic systems, such as capitalism and socialism, play a significant role in shaping culture by determining the distribution of resources and framing society.
- Political Systems: Political systems, such as democracy and dictatorship, moulds culture by determining the distribution of power and influence, and creating laws, policies, and social norms.
- Technology: As Victor Hugo said, “no force on earth can stop an idea whose time has come”. Technology is that rapidly-evolving idea of culture whose time has come. And it is transforming the way people live, work, and interact with one another. Technology is fashioning new forms of communication, commerce, and entertainment, and has the potential to transform cultural practices and beliefs.
Culture is composed of a complex and interrelated set of components that help define its nature and significance. It sub structs the shell for understanding the Culture and Society.
Cultural change and Adaptation
You have to maintain a culture of transformation and stay true to your values
Jeff Weiner
Cultural change refers to the modifications and transformations that occur in a society’s norms, beliefs, values, and practices over time. Cultural change can be driven by various factors, such as technological advancements, exposure to new ideas and ways of life, population growth and migration, and political and economic shifts.
Adaptation, on the other hand, refers to the process by which individuals, groups, and societies adjust to cultural changes. Adaptation can take many forms, such as the adoption of new technologies, the integration of new beliefs and practices into existing cultural norms, or the development of new cultural forms that reflect changing societal needs and values.
Cultural change and adaptation are interconnected processes, as cultural change often drives the need for adaptation, and adaptation in turn can contribute to further cultural change. Both cultural change and adaptation are key aspects of cultural evolution and are essential to the survival and development of human societies. Understanding cultural change and adaptation is a fundamental aspect of the study of anthropology and provides important insights into the dynamics of human cultures and societies over time.
Society
Society refers to a group of individuals living in a definite geographical area and sharing common culture, institutions, and norms. It borders the complex network of relationships, institutions, and systems that shape and influence the behaviour and credence of individuals and groups. Society is dynamic, constantly changing and evolving, and is influenced by a range of factors, including cultural, economic, political, and technological forces.
Components of society
Society is composed of a complex network of relationships and faith systems that builds and influences individuals. The key components of society include:
- Social Institutions: Institutions play a vital role in sculpting and influencing society, providing a foundation for regulating behavior and maintaining social order, peace and harmony. Examples of institutions include the government, the legal system, the education system, and religious organizations.
- Culture and Society: Culture is the indispensable element of society, shaping beliefs, values, and behaviors, and providing a sense of identity and belonging for individuals and groups. Culture and society complement each other. Culture is transmitted through language, education, and other forms of socialization, and is constantly changing and evolving over time.
- Social groups: Society is composed of a range of social groups, including families, organizations, and communities, each of which has its own unique outlook and doctrine.
- Social Stratification: Society is often characterized by social stratification, with individuals and groups occupying different positions in a hierarchical system based on factors such as wealth, power, and status.
- Social Norms: Social norms are informal rules that govern behavior in society, providing a shared understanding of what is acceptable and what is not.
- Social change: Society is constantly changing and evolving, influenced by a range of factors, including cultural, economic, political, and technological forces. Social change can lead to new forms of expression, art, and technology, but can also result in conflict and social upheaval.
Connection between Culture and Society
The interconnection between Culture and Society is complex plus reciprocal, with each molding and guiding the other. Society provides a framework for regulating behavior and maintaining social order, influencing the cultural norms and values that individuals and groups embrace. Meanwhile, culture provides a framework for understanding the beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups, fashioning the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies.
For example, cultural beliefs and values influence the institutions and systems that make up society, such as the legal system, the education system, and religious organizations. At the same time, these institutions and systems shape the cultural beliefs and values of individuals and groups, influencing their sense of identity and belonging.
The relationship between Culture and Society is constantly changing and evolving, with new forms of expression, art, and technology emerging in response to changes in society. Conversely, cultural evolution can drive social change, as new beliefs, values, and behaviors challenge the norms and expectations of society.
The relationship between these two entities; Culture and Society is crucial in constructing the belief systems, values, and behaviors of individuals and amass, and in determining the character of society and the norms and expectations that it consolidates.
Culture and Society: Mutual Influence
The mutual influence of Culture and Society on each other is a shared sort of process. Culture provides a skeleton for understanding the beliefs, values, and behaviours of individuals and groups, while society provides a structure for regulating behaviour and maintaining social order.
- Society influences culture: Society provides a structure for regulating behavior and maintaining social order, shaping the cultural norms and values that individuals and groups embrace. Culture and society influence each other. The institutions and systems that make up society, such as the government, the legal system, and religious organizations, play a central role in shaping and influencing the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
- Culture influences society: Culture shapes the beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups, providing a sense of identity and belonging, and influencing the norms and expectations of society. Culture is transmitted through language, education, and other forms of socialization, and is constantly changing and evolving over time, shaping the evolution of society in response.
Social change and cultural evolution
Society is constantly changing and evolving, influenced by a range of factors, including cultural, economic, political, and technological forces. This social change can result in cultural evolution, with new forms of expression, art, and technology emerging in response to changes in society. Conversely, cultural evolution can drive social change, as new beliefs, values, and behaviours challenge the norms and expectations of society.
Coexistence and Development of Culture and Society
Culture and Society are interdependent and co created, complementing each other in a dynamic and constantly evolving manner. The development of society and culture are intertwined, with each moulding the other with changing time.
Socialization
Culture is transmitted through socialization, the process by which individuals and groups learn and adopt the norms and values of society. This process is influenced by the institutions and systems that make up society, including family, education, religion, and media, which play a central role in shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
Cultural diffusion
The exchange of ideas and cultural practices between individuals and groups is known as cultural diffusion, and it plays a key role in the development of Culture and Society. This process can occur through trade, travel, or other forms of interaction, and it results in the fusion of cultural beliefs, values, and practices, shaping the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies.
Technology and cultural evolution
Technological innovations play a central role in drafting the character of culture and society and the norms and expectations that it embodies. Technology has the potential to shape cultural beliefs, values, and practices, resulting in cultural evolution and social change. For example, the widespread adoption of new technologies, such as the internet and social media, has resulted in new forms of communication, expression, and social interaction, shaping the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies.
Political and economic systems
The political and economic systems that make up culture and society play a crucial role in shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups. For example, political systems can influence the cultural beliefs and values of individuals and groups, shaping the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies. Economic systems, in culture and society on the other hand, can shape the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups, influencing the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies.
Social movements and cultural change
Social movements, such as civil rights movements and feminist movements, have played a central role in shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups, and in driving social change. These movements challenge the existing norms and expectations of society, and they result in the evolution of cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors, shaping the character of society and the norms and expectations that it embodies
Social Relationships/Institutions and Cultural Practices
Social institutions and cultural practices are closely related and interconnected, shaping and influencing each other in a complex and dynamic manner.
- Family: The family is a key social institution that plays a central role in shaping cultural beliefs, values, and practices. Family values and traditions are transmitted through socialization, and they shape the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
- Education: Education is a key social institution that plays a central role in shaping cultural beliefs, values, and practices. Schools, universities, and other institutions of learning provide the foundation for cultural transmission, shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
- Religion: Religion is a key social institution that plays a central role in Culture and Society. Religious institutions, such as churches and temples, serve as the foundation for cultural transmission, shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
- Media: The media is a key social institution that plays a central role. The media, including television, radio, newspapers, and the internet, serve as a source of information and cultural transmission, shaping the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups.
- Government: Government is a key social institution that plays a central role in shaping cultural beliefs, values, and practices. Governments regulate cultural practices and shape the cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors of individuals and groups through laws, policies, and regulations.
Culture and Society in Cross Cultural Perspective
Cultural exchange in Culture and Society refers to the sharing of cultural practices, beliefs, values, and traditions between different cultural groups, while cultural integration refers to the blending and merging of these cultural practices and traditions to create a new, shared cultural identity. Cultural exchange and integration can be facilitated by globalisation, travel, and immigration, and can result in a greater appreciation of cultural differences, increased mutual understanding and a more inclusive and diverse society.
Comparison of Different Cultures in a Society
Anthropology is the study of Culture and Society of humans.It aims to understand the differences and similarities between cultures, their practices. There are many different cultures within a single society, and the way they interact with each other can have a remarkable impact on the society as a whole.
One way to compare different cultures is through their systems of beliefs and values. For example, in a society with a dominant religious culture, the values and beliefs of that religion may influence the laws and social norms of the society. On the other hand, a secular culture may prioritise individual freedom and equality over religious beliefs.
Another way to compare cultures is through their economic systems. For example, in a capitalist culture, individuals are driven by the pursuit of profit and economic success. In contrast, a socialist culture may prioritise the well-being of the community as a whole over the success of individual members.
Language is also a significant aspect of culture. In a multilingual society, different languages may be spoken by different cultural groups, and the use of different languages may serve as a marker of cultural identity. For example, in a society with multiple indigenous cultures, the use of indigenous languages may be an important aspect of preserving cultural heritage.
The relationship between different cultures within a society can also impact the overall social dynamics. In some societies, cultural groups may exist in relative harmony, with little conflict or competition between them. In others, there may be tensions and conflicts between cultural groups, leading to feelings of marginalisation or discrimination.
It’s worth noting that culture is not static, but rather is constantly evolving. As individuals interact with each other and with the wider world, cultural practices, values, and beliefs change. In a multicultural society, this can lead to cultural exchange, where individuals from different cultural backgrounds learn from and influence each other.
In conclusion, the comparison of different cultures within a society is an important aspect of anthropology. By studying the differences and similarities between cultures, anthropologists can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of human societies and the ways in which culture formulates our experiences and identities.
History of Culture and society
We study humans from both past and present, their Culture and Society formed by them in Anthropology.The history of anthropology as a discipline dates back to the 19th century, when it was first established as a separate academic field in Europe. However, the roots of anthropology can be traced back much further, to the ancient Greeks, who made significant contributions to the study of human culture and society.
In the 19th century, anthropology was heavily influenced by the ideas of evolution and social Darwinism, which viewed different cultures as evolving along a linear progression from “savagery” to “civilization.”
This perspective was used to justify colonialism and imperialism, as the colonising powers saw themselves as bringing “civilization” to “uncivilised” peoples. Anthropologists of this period conducted extensive fieldwork, mostly in colonial settings, and produced rich descriptions of the cultures and societies they encountered.
In the early 20th century, anthropology underwent significant changes as a result of the cultural relativism movement.
Anthropologists began to question the idea of a single, universal standard of progress and instead argued that each culture must be understood on its own terms. This perspective led to the development of cultural anthropology, which focused on the study of living cultures and their practices and beliefs.
Cultural anthropologists conducted fieldwork in communities around the world, often living among their subjects for extended periods of time. This approach allowed them to gain a deep understanding of the cultural systems and practices of the communities they studied.
One of the most influential cultural anthropologists of this period was Franz Boas, who is considered the founder of American anthropology. Boas was a strong advocate of cultural relativism and was critical of the idea that cultures could be ranked along a linear progression of development in culture and society.
Another major development in anthropology was the shift from a focus on descriptive ethnography to a more analytical approach that emphasised the importance of understanding cultural systems and their interconnections. This led to the development of structural-functionalism and cultural materialism, which sought to explain the functions and relationships of cultural systems.
Anthropologists in this tradition saw cultures as integrated systems that operated to meet the basic needs of their members, and sought to understand how different cultural practices and beliefs fit together to form a coherent whole.
In the mid-20th century, anthropology was further influenced by developments in archaeology, linguistics, and physical anthropology, which together formed the subfield of anthropological archaeology. This new approach aimed to integrate all of the different aspects of human culture and society, from their material remains to their linguistic and social practices.
Anthropologists in this tradition saw culture as holistic systems that could be studied from multiple perspectives, and sought to understand the relationships between different aspects of human society, such as their economies, languages, and political systems.
In recent decades, anthropology has expanded to encompass new areas of study, such as medical anthropology, environmental anthropology, and feminist anthropology.
These subfields have helped to broaden the scope of the discipline and provide new insights into the complex relationships between human cultures and the natural world, as well as the ways in which gender, power, and inequality carves human Culture and Society.
- Medical anthropology, for example, assesses the intersections between culture and health, and seeks to understand how cultural beliefs and practices build the ways in which people experience and understand illness.
- Environmental anthropology examines the relationships between human culture and the natural world, and seeks to understand the cultural and social extent of environmental issues such as climate change and resource depletion.
- Feminist anthropology is concerned with the ways in which gender forms human culture and society, and also seeks to understand the ways in which gender intersects with other social and cultural dimensions, such as race, class, and sexual orientation.
Today, anthropology continues to be a dynamic and evolving field, with a rich and diverse tradition of scholarship and research that seeks to understand the complexities of human Culture and Society.
Impacts of Globalization on Culture and Society
Globalization has had a profound impact on Culture and Society, affecting the beliefs, values, traditions, and practices of people across the world. The impact of globalization on Culture and Society can be both positive and negative.
Positive impacts of Globalization on culture include:
- Exposure to new cultures: Globalization has provided people with the opportunity to learn about and experience new cultures, broadening their horizons and increasing cross-cultural understanding.
- Preservation of cultural heritage: Globalization has helped preserve cultural heritage, as traditional practices and cultural traditions are shared and passed onto future generations of the Culture and Society.
- Cultural hybridization: Globalization has led to the creation of new cultural hybrid forms, where cultural practices and traditions are combined to create unique and dynamic cultural expressions.
Globalisation has also had negative impacts on culture, including
- Homogenization: Globalization has led to the homogenization of cultures, with dominant cultures spreading across the world and pushing aside traditional cultures.
- Cultural appropriation: Globalization has led to the appropriation of cultural practices and traditions, with cultural expressions being co-opted and commodified for commercial purposes in Culture and Society.
While globalization has provided opportunities for cultural exchange and preservation, it has also led to the homogenization of cultures and the appropriation of cultural practices and traditions in Culture and Society.
Conclusion
In terms of their relationship, Culture and Society are two components that complement one another. Culture is ingrained in both the physical environment as well as in the social institutions of society, manifesting itself in socioeconomic structures moulds it for the organisation of social relationships. Culture structures social dynamics and organises material experiences. However culture is also the lens through which the social environment is perceived, analysed, and comprehended. Culture is therefore something more fundamental than ideological superstructure. In a particular society, culture is created within the confines of the socio-economic system. A society’s many groups and classes engage in a continuous cultural process that also has an impact on the social structure. This is the whole relationship between Culture and Society.




