AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Gender Issues
Gender issues are problems that come up when people are treated unfairly just because of their gender. Think about situations
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Political Anthropology is the study of the relationship between power, politics, and culture in human societies. This category covers topics related to political systems and institutions, including forms of governance, decision-making, and conflict resolution. From exploring the cultural dimensions of political power to examining the impact of colonialism and globalization on political systems, this category provides insights into the diverse and complex nature of human politics.

Gender issues are problems that come up when people are treated unfairly just because of their gender. Think about situations

The term, popularized by the historical scientist Peter Turchin, describes a simple but dangerous imbalance. It occurs when a

Honor killings, a deeply disturbing cultural phenomenon, are murders committed under the pretext of preserving the perceived honor of a family or community. They occur when the victim, usually a female, is believed to have brought

Customary law is a fascinating subject in anthropology, as it offers insight into the structures of societies and cultures. This type of law, though not formally codified like statutory law, holds significant sway over local practices and behaviors.

The human legal framework's evolution is a fascinating journey from rudimentary principles of "primitive law" to complex edifices of "modern law". A grasp of this transformation is not just about understanding legal systems but also appreciating human evolution, culture, and society.

The study of dispute resolution mechanisms in pre-literate societies offers an important window into the complexity of these societies and their sophisticated approach to maintaining social order. Despite their lack of written laws or formal institutions, these societies developed effective systems for resolving disputes, preventing conflicts, and upholding social norms.
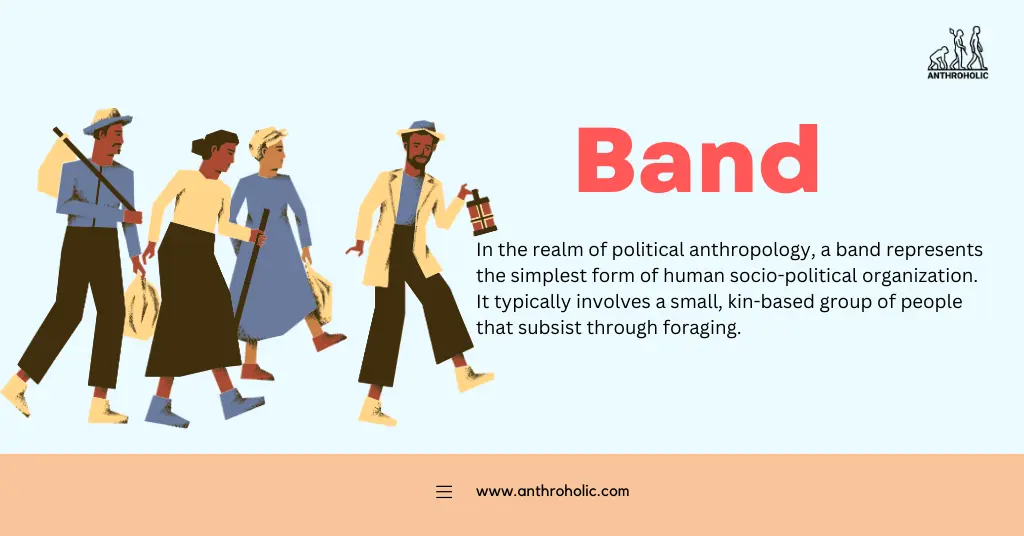
In the realm of political anthropology, a band represents the simplest form of human socio-political organization. It typically involves a small, kin-based group of people that subsist through foraging.

Political systems have come a long way from the egalitarian societies of our prehistoric ancestors to the complex structures we see today. As we navigate the digital revolution and confront global challenges such as climate change, these systems will continue to evolve.

Centralised and decentralised political systems represent different approaches to governance and power distribution, each with its inherent benefits and challenges. Anthropology helps us understand these systems within their socio-cultural contexts, providing insights into their influence on society's organisation and functioning.

The dichotomy of state and stateless political systems provides a compelling lens through which to view human political organization. As anthropology continues to explore these diverse forms of governance, it sheds light on the remarkable capacity of societies to adapt and create structures that reflect their unique circumstances and values.

The structures of egalitarian and non-egalitarian societies highlight different aspects of human social organization. While egalitarian societies reflect values of equality and shared responsibility, non-egalitarian societies underscore the human inclination towards structure, hierarchy, and individual achievement.

Conflict is an intrinsic element of social relationships, and how societies handle disputes and disagreements speaks volumes about their culture, values, and social structures. Anthropology, the study of human societies and cultures, offers a lens through which we can better understand and evaluate the diverse peaceful means of dispute settlement.