AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Dryopithecus
Dryopithecus, a member of the extinct great ape family, holds a significant place in the study of hominid evolution. Their fossilized remains, often discovered in
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, driven by mechanisms such as mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift. This category covers the history of evolutionary thought, the mechanisms of evolution, and the diversity of life on Earth. From exploring the origins of species to understanding the evolutionary relationships between different organisms, learn about the science behind the history of life on our planet.

Dryopithecus, a member of the extinct great ape family, holds a significant place in the study of hominid evolution. Their fossilized remains, often discovered in

The Cro-Magnon people are among the earliest known examples of Homo sapiens in Europe. Their remains, along with impressive examples of their art and other artifacts, have helped anthropologists understand the human journey.

Australopithecus is a genus of hominins that existed between approximately 4.2 and 1.2 million years ago. The name, which translates to 'southern ape',

Lucy’s fossil remains were unearthed on November 24, 1974, in the Hadar region of the Afar

The first recognized Neanderthal fossils were discovered in 1856 in the Neander Valley (or Neandertal) near Düsseldorf, Germany.
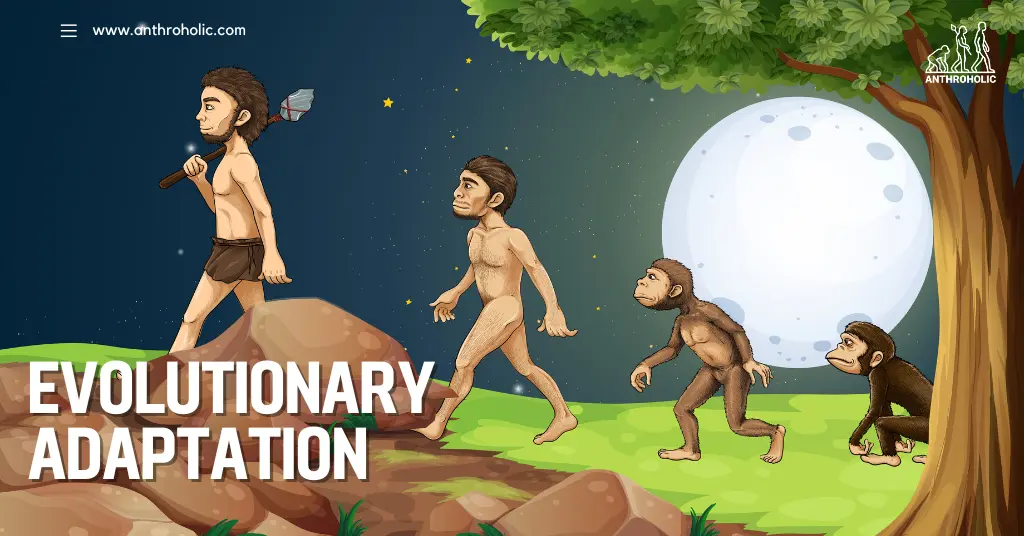
Evolutionary adaptation, also known simply as adaptation, refers to the process by which organisms evolve traits and behaviors that help them survive and thrive in their environment. This process is driven by natural selection, a core mechanism of evolution

The emergence of life on Earth is an expansive topic that dives into the very origins of our existence. Around 4.6 billion years ago, our planet formed in the chaotic heart of a stellar nursery. Earth's initial conditions were inhospitable for life as we understand it today

The Theory of Viruses presents an unconventional yet intriguing perspective on the evolution of life. This perspective posits that viruses, typically seen as parasitic agents, are central to the genesis and development of life.

Understanding the formation of Earth is a key to grasping our planetary history and the processes that have led to our present condition. Our planet came into existence approximately 4.54 billion years ago, formed from the dust and gas of the nascent solar system.

Mendelism is the principles of genetics, that determine how traits are passed from generation to generation, find their roots in the mid-19th-century work of Gregor Mendel. His pioneering research on pea plants has been foundational to the field, leading to the development of what we now term "Mendelism."
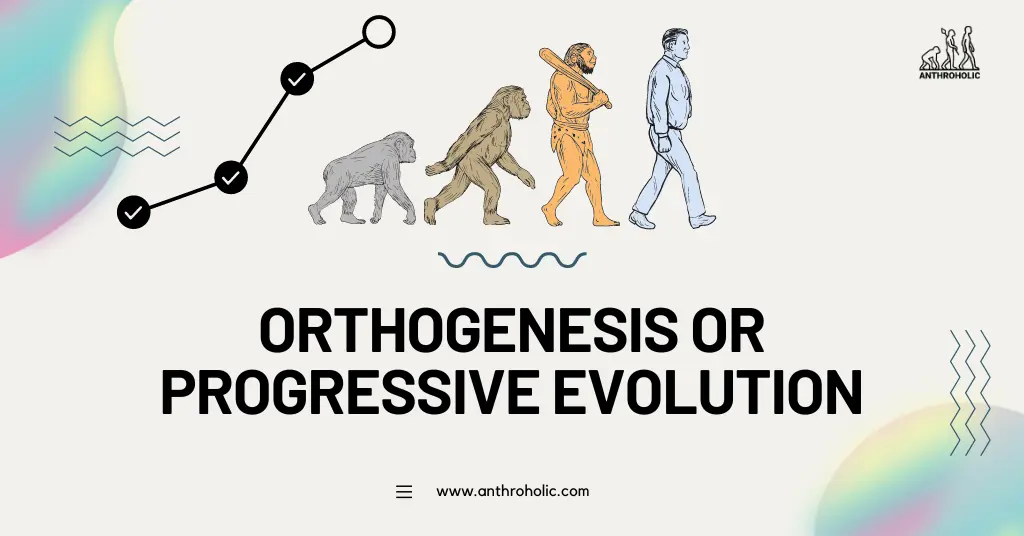
Orthogenesis, also known as Progressive Evolution, is a biological theory that suggests species evolution follows a predetermined path, leading to a specific endpoint.
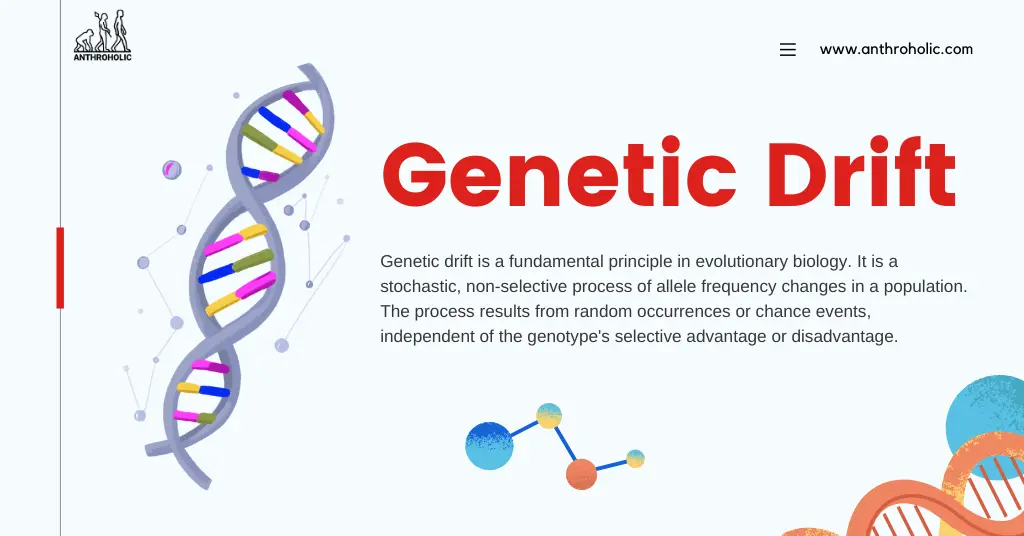
Genetic drift is a process of random sampling. Every generation, alleles are sampled from the existing gene pool to create the next generation. Due to random chance, some alleles get over or underrepresented, leading to changes in their frequency in the population.