AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Language Typology
Language Typology is the field of linguistics and linguistic anthropology that classifies languages according to their structural features
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
"Exploring the Diversity of Human Culture: Insights from Anthropology"

Language Typology is the field of linguistics and linguistic anthropology that classifies languages according to their structural features
That invisible bridge between a symbol and its meaning is the heart of Semantics.
WriteMyEssay.com presents itself as a flexible academic writing platform offering a wide range of services for students, from essays

Subsistence and Gender is a core thematic area in anthropology that examines how different modes of food production such as foraging, horticulture, pastoralism,

In a world increasingly dominated by digital saturation, urban congestion, and ecological crisis, the concept of Primitivism has experienced a powerful resurgence.

For decades, the field of Linguistic Anthropology has been captivated by a singular, provocative question: Is the capacity for language a uniquely human trait

From the high-stakes debates of the ancient Greek agora to the carefully curated viral clips of 21st-century digital activists, the ability to
In the vast landscape of anthropological study, few elements of human interaction are as potent yet as frequently misunderstood as the gaze. Oculesics,

Anthropology now faces a tension between fast technical progress and moral duty to the people it studies. AI tools promise speed and scale,

In the digital age, the air we breathe is saturated with symbols. From the pithy slogans of 24-hour news tickers to the algorithmic brevity of a viral "reel," language

In an increasingly globalized world, the ability to decode the silent languages of culture is no longer just an academic pursuit; it is a survival skill.
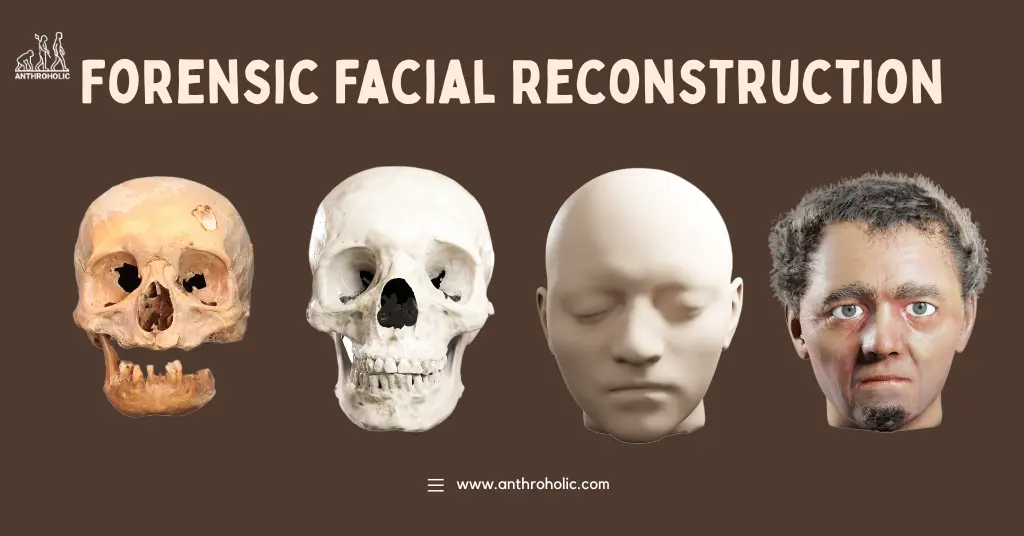
Imagine holding a skull a silent, anonymous relic of a life lost.