AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
Branches of Human Genetics
Human genetics is a vast and complex field of study that aims to understand the inheritance of traits in humans. It encompasses various branches that explore different aspects of genetics, from the study of the structure and function of genes to the analysis of how genetic variations contribute to human diseases. In this article, we will discuss the different branches of human genetics and what they entail.
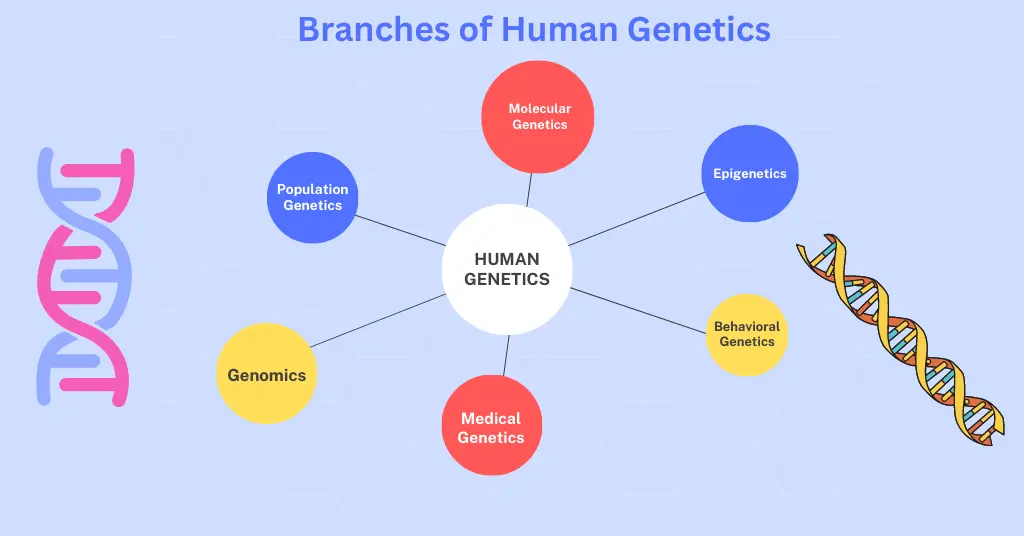
Molecular genetics
The study of the molecular makeup and operation of genes is known as molecular genetics. It examines the chemical and physical properties of DNA, RNA, and proteins that make up the genetic code. The field of molecular genetics has revolutionized our understanding of genetics by enabling researchers to manipulate genes and create genetically modified organisms. It has also led to the development of new technologies, such as genetic engineering and gene therapy, which have the potential to treat genetic diseases.
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of genetic variation and evolution within populations. It examines how genes are distributed and change over time in response to various factors, such as mutation, migration, natural selection, and genetic drift. Population genetics is important in understanding the genetic basis of complex traits and diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. It also has implications for conservation biology, as it helps to identify endangered populations and preserve genetic diversity.
Genomics
Genomics is the study of the entire set of genes in an organism, known as the genome. It includes the analysis of gene structure, function, and expression, as well as the identification of genetic variations that are associated with diseases. Genomics has led to significant advances in medicine, such as the development of personalized medicine and the identification of new drug targets. It has also revolutionized our understanding of human evolution, by providing insights into our ancestral history and the genetic differences between populations.
Medical genetics
Medical genetics is the study of the genetic basis of human diseases. It includes the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease. Medical genetics also involves genetic counseling, which helps individuals and families understand the risks and implications of inherited genetic conditions. Medical genetics is a rapidly advancing field, with new genetic tests and therapies being developed every day.
Behavioral genetics
Behavioral genetics is the study of the genetic and environmental factors that influence human behavior. It examines the role of genes in various behavioral traits, such as intelligence, personality, and mental health. Behavioral genetics has important implications for understanding the nature vs. nurture debate, as it helps to identify the relative contributions of genetic and environmental factors to behavior. It also has implications for the development of personalized education and mental health interventions.
Epigenetics
The study of heritable variations in gene expression that are not brought on by variations in DNA sequence is known as epigenetics. It examines how environmental factors, such as diet, stress, and toxins, can modify the expression of genes and influence disease risk. Epigenetic changes are important in development, aging, and disease, and may provide new targets for therapeutic intervention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, human genetics is a fascinating and complex field of study that encompasses various branches, each with its unique focus and applications. From the study of the structure and function of genes to the analysis of genetic variations that contribute to human diseases, human genetics has led to significant advances in medicine, biology, and technology. Understanding the different branches of human genetics is essential to appreciate the broad scope of genetics research and its impact on our lives.



