AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
Microevolution
Microevolution is the study of small-scale changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, driven by mechanisms such as mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift. This category covers the history of evolutionary thought, the mechanisms of evolution, and the diversity of life on Earth. From exploring the origins of species to understanding the evolutionary relationships between different organisms, learn about the science behind the history of life on our planet.

Microevolution is the study of small-scale changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.

The Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis, also known as the primordial soup theory, proposes that life on Earth originated from simple organic compounds that formed in the atmosphere and oceans of the early Earth.
Theories of evolution attempt to explain how species have changed over time and how new species arise.
The Theory of Epigenesis is a scientific concept that seeks to explain the origin and development of organisms through the gradual differentiation of cells.

Macroevolution refers to the long-term patterns and processes of evolution that occur over geological time scales, typically involving the formation of new species and the diversification of entire groups of organisms.

The theory of isolation is a post Darwinian theory put forth by Moritz Wagner. Wagner believed that Darwin was not able to explain the concept of speciation completely.

The theory of spontaneous generation is the idea that living organisms originated from seemingly non-living beings, or even totally inorganic matter.

Molecular evolution is the study of the changes that occur in DNA and protein sequences over time, and how these changes relate to the evolutionary history and relationships of different species.

According to the neutral theory of evolution, the bulk of molecular variation has no influence on fitness, so random processes are the most likely cause of genetic variation.
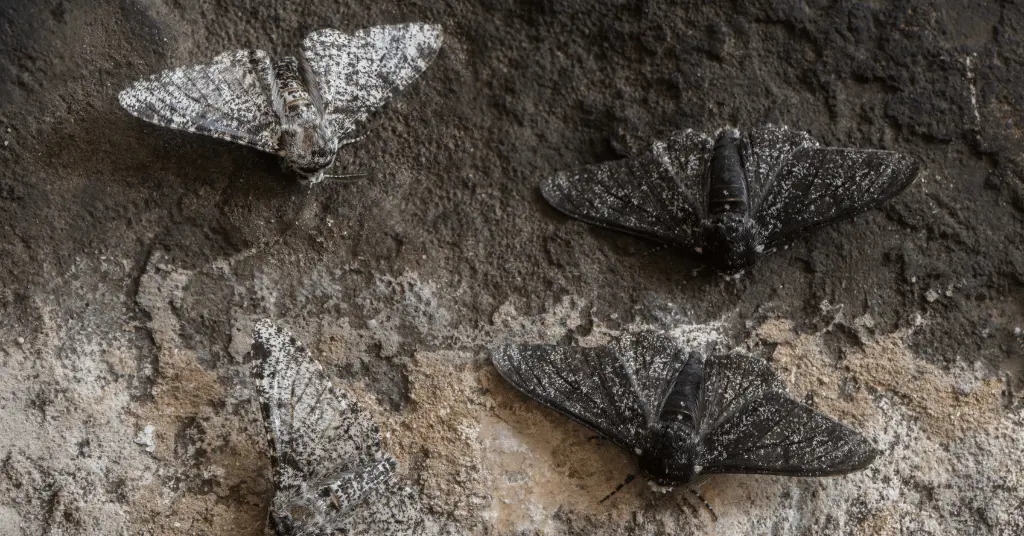

When artificial impacts on natural selection have caused a species' color to change, it is known as industrial melanism.

Hugo de Vries, a Dutch botanist and geneticist, first put out the theory of mutation stating that the new species emerge
In-depth inquiries into the ancestry of Homo sapiens, or modern humans, have been done throughout history. One method is the "multi-regional hypothesis of human evolution".