AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Paranthropus
Paranthropus is a genus of extinct hominins that lived in Africa roughly between 2.7 and 1.0 million years ago.
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM

Paranthropus is a genus of extinct hominins that lived in Africa roughly between 2.7 and 1.0 million years ago.

Dryopithecus, a member of the extinct great ape family, holds a significant place in the study of hominid evolution. Their fossilized remains, often discovered in

Australopithecus is a genus of hominins that existed between approximately 4.2 and 1.2 million years ago. The name, which translates to 'southern ape',

The first fossil fragments attributed to Ramapithecus were discovered in 1932 by British paleontologist G. Edward Lewis in the Siwalik Hills of northern India.

Nicknamed “The Handy Man,” Homo habilis lived in Africa about 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago, bridging the gap between the more ape-like

From hunting and gathering to the industrial stage, eco-cultural adaptations have shaped human civilization in profound ways. Understanding these adaptations provides insight into the complex relationship between humans and their environment across history.

Cultural evolution is a concept that attempts to explain the way societies develop over time, emphasizing how cultural practices, ideas, and technologies change and spread across generations. This understanding of cultural evolution provides a lens through which we can comprehend the broad outlines of prehistoric cultures.
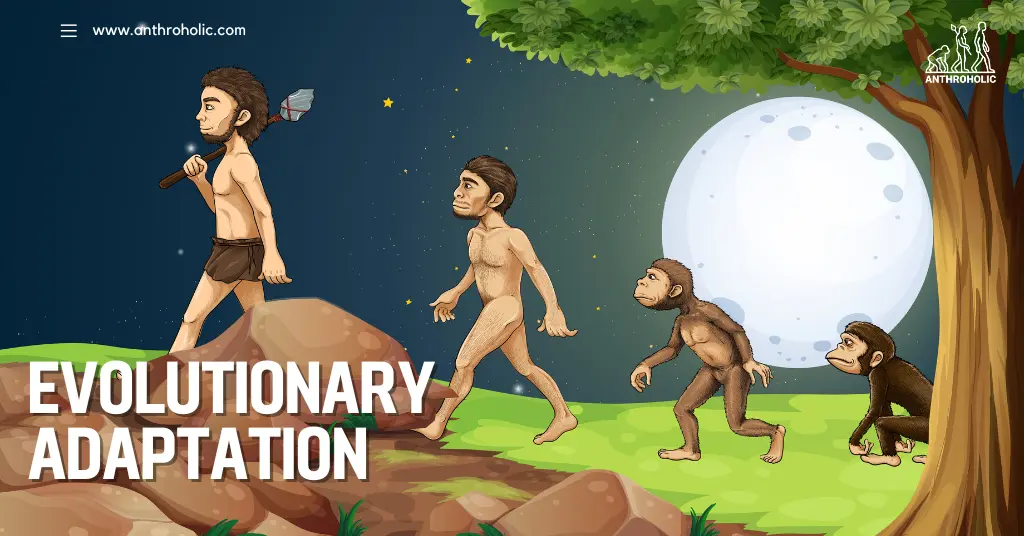
Evolutionary adaptation, also known simply as adaptation, refers to the process by which organisms evolve traits and behaviors that help them survive and thrive in their environment. This process is driven by natural selection, a core mechanism of evolution

The emergence of life on Earth is an expansive topic that dives into the very origins of our existence. Around 4.6 billion years ago, our planet formed in the chaotic heart of a stellar nursery. Earth's initial conditions were inhospitable for life as we understand it today

Human's place in animal kingdom is determined by the biological classification system called taxonomy. Human beings, often considered a unique entity due to our complex intellectual capabilities and cultural systems, belong to the vast and diverse animal kingdom

The Theory of Viruses presents an unconventional yet intriguing perspective on the evolution of life. This perspective posits that viruses, typically seen as parasitic agents, are central to the genesis and development of life.

Understanding the formation of Earth is a key to grasping our planetary history and the processes that have led to our present condition. Our planet came into existence approximately 4.54 billion years ago, formed from the dust and gas of the nascent solar system.