AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
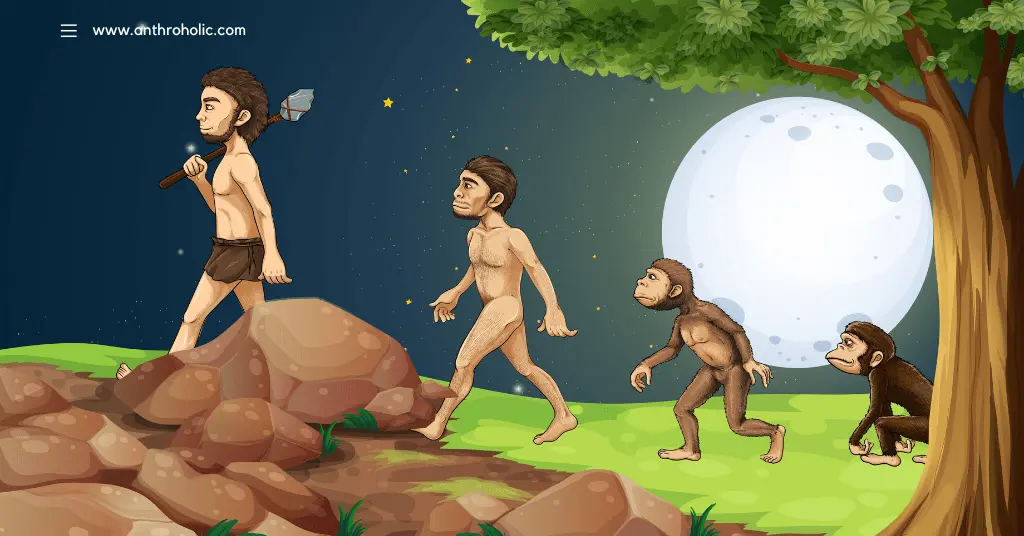

Human Evolution
Human evolution is a broad field of study that explores the biological evolution of Homo sapiens and our close ancestors, dating from the time our lineage diverged from that of chimpanzees, about six to seven million years ago.