AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a process of examining the patterns of inheritance of genetic traits or diseases in families.
+91-7303290503, +91-9557169661 | MON to SUN 10:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Genetics is the scientific study of heredity, gene structure, and function. This category delves into the fundamental principles of genetics, including topics such as DNA, genetic variation, and the regulation of gene expression. From exploring the genetic basis of human traits and diseases to understanding the role of genetics in evolution, learn about the science of heredity and its impact on our lives.

Pedigree analysis is a process of examining the patterns of inheritance of genetic traits or diseases in families.

Genomatics is an interdisciplinary field that combines genomics, bioinformatics, and systems biology to analyze and interpret genomic data, ultimately facilitating a better understanding
Eugenics is a term that refers to the study or practice of improving the genetic quality of the human population by selective breeding, genetic engineering, or other means.

Monozygotic twins, or identical twins, are siblings who are formed from a single fertilized egg that divides into two identical embryos during early development.

DNA is also known as the biological blueprint of life while DNA typing is also known by various names such as DNA Profiling, genotyping or identity testing.

Genetic polymorphism is the occurrence of different gene or DNA sequence forms in a population. It results from natural variation and mutations, creating genetic code differences.

Our understanding of genetics is aided by the principle of inheritance and variation. The study of genes or features
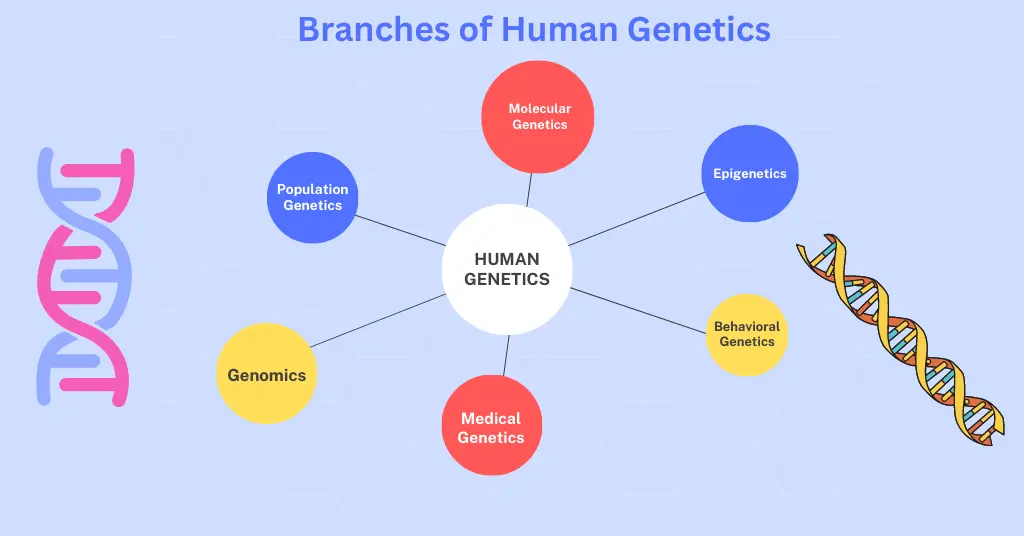
Human genetics is a vast and complex field of study that aims to understand the inheritance of traits in humans.
Chromosomal analysis can reveal important details regarding genetic diversity in humans, population genetics, and the forces that drive evolution.
According to Colin Renfrew, the application of molecular population genetics approaches to the study of human evolution is referred to as "archaeogenetics."