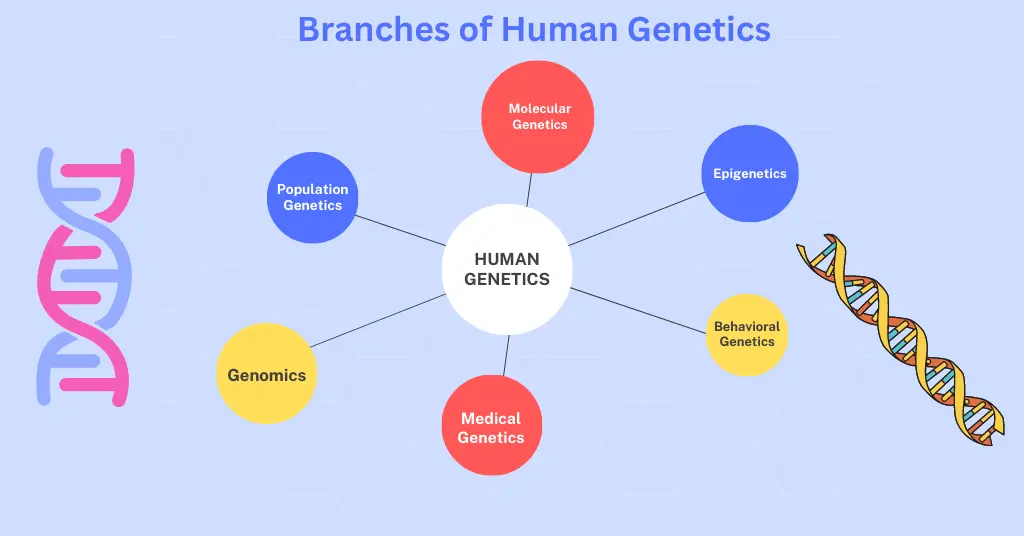
AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now
Eugenics
Eugenics is a term that refers to the study or practice of improving the genetic quality of the human population by selective breeding, genetic engineering, or other means.