AI Answer Evaluation Platform Live Now. Try Free Answer Evaluation Now

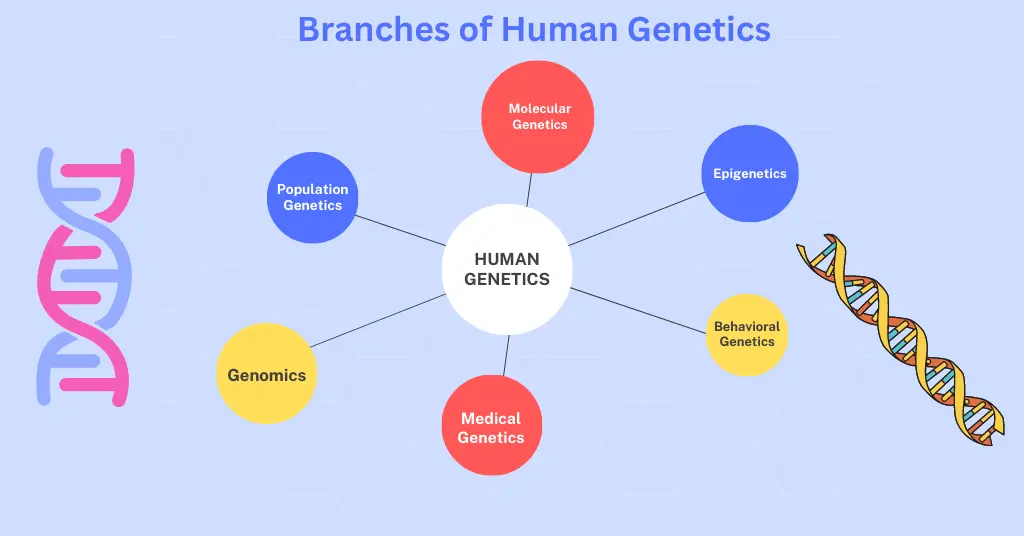
Theory of Recapitulation or Embryological Parallelism
The Theory of Recapitulation, also known as Embryological Parallelism or Biogenetic Law, is a scientific theory that proposes a parallelism between the